How and Why to Prevent ChatGPT and Its Plugins from Crawling Your Website
As an SMB owner, it’s crucial to be in control of who has access to your website and how it’s indexed. While ChatGPT and related plugins offer a wide range of utilities and benefits, there might be instances when you’d prefer they not crawl or index your website. In this post, I’ll break down the simple steps to prevent ChatGPT and its plugins from accessing your site and discuss why you might want to take such an action.
First and Foremost – Why Prevent ChatGPT from Crawling Your Site?
Before we delve into the how-to, it’s important to understand why you might want to restrict access:
Privacy Concerns: Your website might host proprietary or sensitive information that you’d rather not have machine learning models accessing or potentially storing.
Bandwidth Issues: Web crawlers consume server resources. If you have multiple bots crawling your site, it can slow down the performance for genuine users.
Relevance: If your site isn’t relevant to the purposes of the tool or plugin, you might prefer to keep it off the radar to ensure more targeted content for your intended audience.
Steps to Prevent ChatGPT and its Plugins from Crawling Your Site:
Robots.txt File:
The most common and straightforward method to control web crawler access is through a robots.txt file.
This file provides directives to web robots about which parts of the site should not be processed. To disallow all web robots (including ChatGPT plugins) from accessing your site, add the following lines to your robots.txt file:

If you only want to prevent ChatGPT or a specific plugin from accessing your site:

Replace `ChatGPT-Agent-Name` with the name of the specific bot or plugin you want to block.
Meta Robots Tag:
If you want to prevent crawling of specific pages rather than the entire website, you can use the Meta Robots Tag within the HTML of those pages. Add the following line to the `<head>` section:
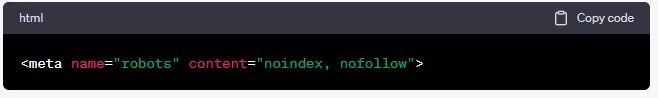
This tag instructs search engines and web robots not to index or follow the links on the page.
Server-side Restrictions:
For more advanced users, you can set up rules within your server configuration (like .htaccess for Apache servers) to block specific user agents or IP addresses.
Reach Out to the Source:
If you’re uncertain about a specific ChatGPT-related agent, it might be helpful to reach out directly to the organization or developer behind the plugin. They can provide information about the bot’s user-agent name or offer other insights.
Final Thoughts:
Managing who and what has access to your website is essential for ensuring a positive user experience, maintaining your site’s security, and preserving bandwidth. While tools and plugins like ChatGPT have a wide array of applications, it’s up to you as the website owner to determine if and how they interact with your content. Remember always to monitor your site’s traffic and adjust your settings as needed.
Here’s some more articles you may find interesting!